Cardboard is a versatile material that is found in almost every household and business worldwide. It has been praised for its insulating ability, but only on a small scale. Still, when something is so affordable and freely available, it’s easy to look at how we can use it for larger-scale applications.
However, before you stuff your walls with broken-down empty boxes, there are several factors you need to consider.

Cardboard has insulating abilities but its vulnerability to mold, moisture, fire, and ripping means that it is not an acceptable insulation material. However, when processed, cardboard becomes a well-known and acceptable form of insulation known as cellulose.
Cardboard Has Insulating Properties
Cardboard is made from cellulose or wood fiber. Considering that both wood and cellulose are excellent insulators, cardboard can effectively keep heat in or out of a structure.
Corrugated cardboard usually has a fluted-like structure comprising layers of kraft paper with air pockets trapped in between.
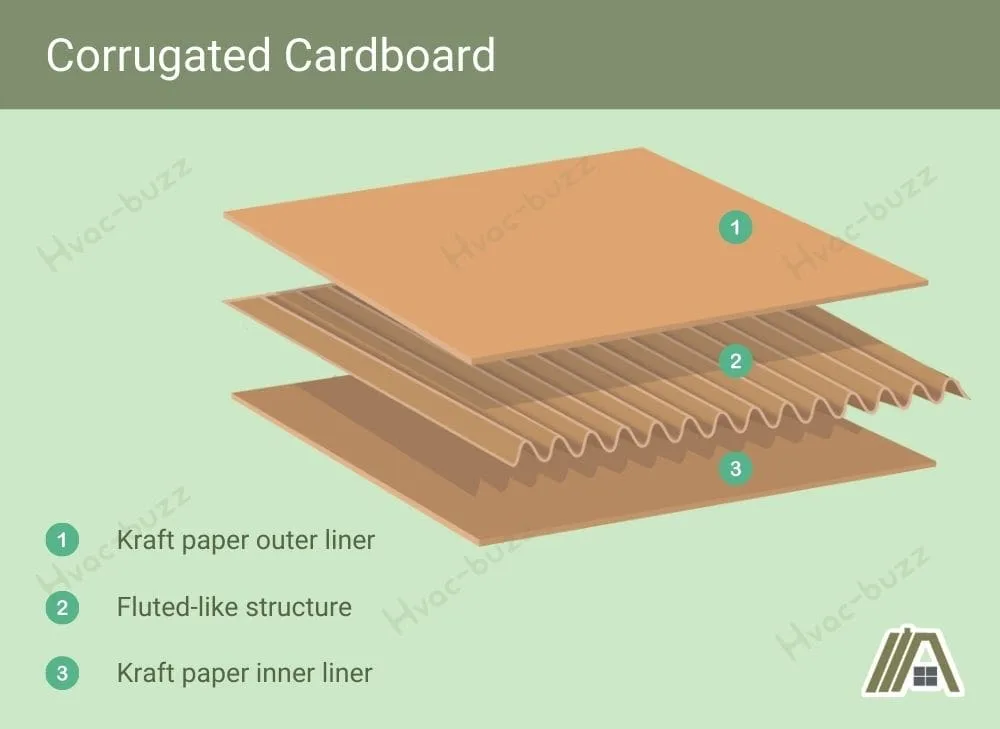
These tightly packed fibers create air pockets that prevent heat from transferring in the same way as the air pockets in fiberglass.
The R-value of cardboard ranges from less than R-0 to R-4 per inch, depending on who you ask. From about R2.5 to R4, you are reaching the same thermal resistive capability as proper insulation material.
However, while cardboard can be a comparatively good thermal insulator, it may not always be the best choice for all insulation needs. This is because it also has some less desirable qualities, which we’ll discuss in the next section.
Cardboard Is Not Appropriate for Insulating a House
Cardboard can provide some insulation but is not appropriate for insulating a house as it is not designed to be a long-term solution and will quickly deteriorate in most environments.
Detailed below are some factors that make it less suitable for insulation.
Moisture
Cardboard comprises paper fibers pressed together and held in place with adhesives. The paper fibers are porous and highly absorbent, making them susceptible to moisture absorption.
When cardboard absorbs moisture, the adhesives that hold the fibers together weaken, causing the cardboard to disintegrate and become structurally unsound.

The cardboard may disintegrate, bend out of shape, and shift. If used as insulation, this would result in the insulation compressing, tearing and splitting, and/or falling down.
Aside from that, the porous nature of cardboard can make drying difficult. As cardboard dries slowly in humid climates, it may never completely dry out, making it unusable.
Mold
As mentioned, cardboard is primarily made from cellulose fibers. When these are broken down, it becomes an ideal food source for mold and other fungi.
When the reason for break down is moisture, another great factor for encouraging mold growth, it’s almost guaranteed that damp cardboard will become moldy.
Mold growth can cause various health concerns, including respiratory and allergic reactions. It also weakens the structural integrity of a building and may lead to costly repairs.
Fire Risk
Cardboard is highly combustible. Below is a video of a cardboard fire test.
When used as insulation, cardboard can create a potential fire hazard if it comes into contact with a heat source, electrical wires, or an open flame, all of which are commonly encountered in a home.
Once ignited, the cardboard insulation is in a position to readily spread the fire throughout the house. Worse still, it may burn unnoticed within the walls. This means that by the time you figure out there is a fire, the damage to the structure of the home may be extreme.
Ripping/Tearing
Even when it’s not wet, cardboard is still prone to ripping and tearing, which can compromise its ability to provide insulation.
The paper pulp making up cardboard is not a strong material, making them more prone to tearing and punctures. When exposed to moisture or changes in temperature, the fibers inside can further weaken.
When cardboard rips or tears, it creates holes in the insulation barrier, allowing heat to pass through readily.
In addition, a torn piece of cardboard causes the fibers and air pockets of the cardboard to become disrupted and unable to insulate and maintain a consistent temperature.
Cellulose Insulation Is Made up of Cardboard
While cardboard cannot be used as insulation, it can be used for insulation.
Cardboard can be transformed into very effective and durable cellulose insulation. Many of the risks associated with using cardboard as insulation are minimized when it’s in the form of cellulose.
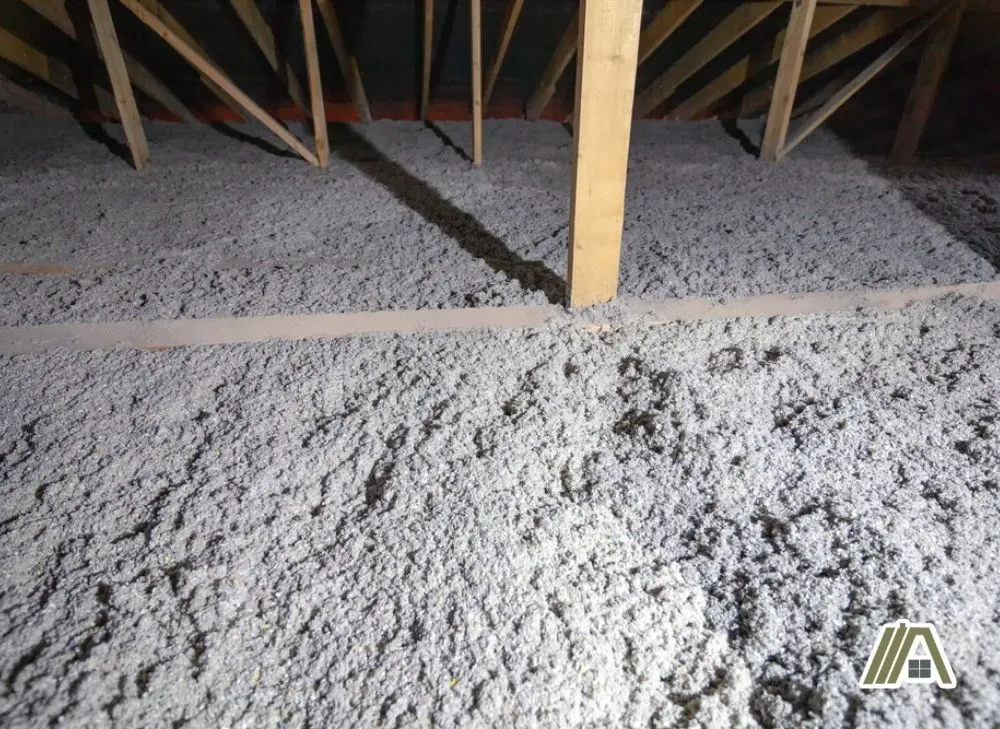

Cellulose production involves shredding the cardboard into small pieces using a hammermill.
The pieces are treated with boric acid/powder, which guards against mold growth as the chemical contains natural anti-fungal properties. This treatment minimizes the risk of mold growing on the insulation.
Boric acid also works as a fire-retardant by forming a glassy layer on the surface of cellulose when exposed to high temperatures. This layer helps to protect the cellulose from catching fire and burning, which cardboard in its natural state cannot offer.
This treatment is also effective at combating the issue of moisture. While cellulose insulation is not water-resistant, it’s still a great insulation option because of its ability to slowly absorb and wick moisture.
This feature allows it to maintain its insulating properties even when exposed to moisture (this does not make wet insulation acceptable to leave).
In the final stage, cellulose is mixed with a binding agent that causes the fibers to interlock. This interlocking creates a dense, durable product that eliminates ripping and tearing risks.
In addition, cellulose insulation is usually in loose-fill form, which means that ripping and tearing are not as big of a problem.
