AC ceiling fans have been around for about a century. The fact that they are still being installed in homes despite the invention and improvement of air conditioners and HVAC systems, shows that they are still a valuable and effective device. Yet, they may finally be in danger of being replaced by the newest development in ceiling fan design and engineering.
Ceiling fans are now being sold with DC motors, which make them more energy-efficient, compact, and quieter. However, the upfront cost is generally much higher for DC fans than it is for AC fans. So, what are the power consumption comparisons, and does saving on running costs cover the purchase price of the DC fans?

DC ceiling fans use up to 70% less power than AC ceiling fans because they function with direct current and also have a magnet system to assist rotor movement.
DC Fans Use Less Power
DC fans to consume up to 70% less power than an AC fan.
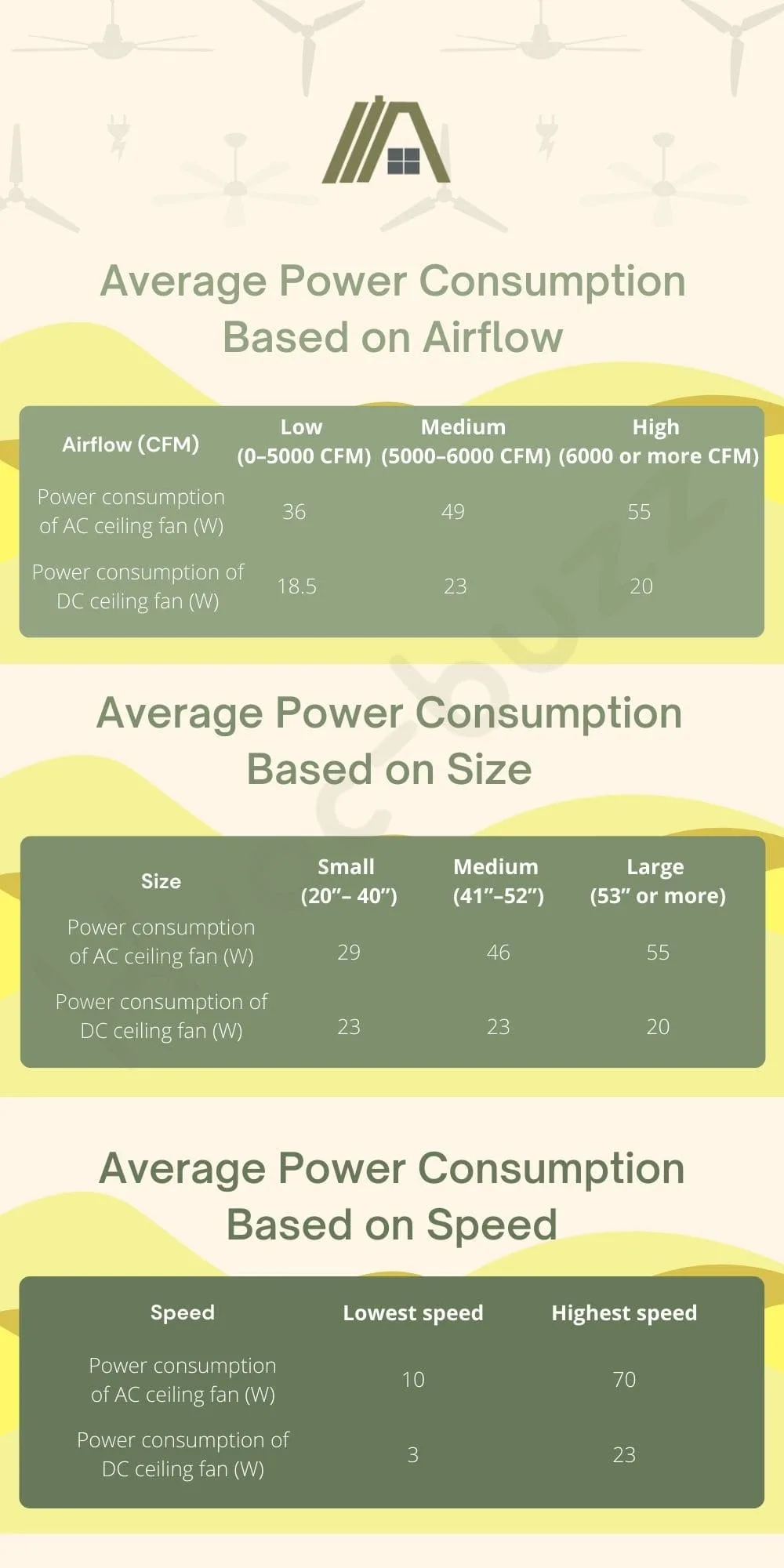
Average Power Consumption Based on Airflow
| Airflow (CFM) | Low (0–5000 CFM) | Medium (5000–6000 CFM) | High (6000 or more CFM) |
| Power consumption of AC ceiling fan (W) | 36 | 49 | 55 |
| Power consumption of DC ceiling fan (W) | 18.5 | 23 | 20 |
Average Power Consumption Based on Size
| Size | Small (20”– 40”) | Medium (41”–52”) | Large (53” or more) |
| Power consumption of AC ceiling fan (W) | 29 | 46 | 55 |
| Power consumption of DC ceiling fan (W) | 23 | 23 | 20 |
Average Power Consumption Based on Speed
| Speed | Lowest speed | Highest speed |
| Power consumption of AC ceiling fan (W) | 10 | 70 |
| Power consumption of DC ceiling fan (W) | 3 | 23 |
Why Do DC Fans Consume Less Power?
Alternating current rapidly changes direction while it flows. This results in energy loss. Because DC motors use direct current rather than alternating current, less energy is lost and more of what is supplied is available to be converted into work (power).
In addition, the rotor of DC fans utilizes magnets of opposite polarity to support the motor-driven blade rotation. These magnets are positioned so that the natural attraction between the magnets pulls the blades in a specific direction without the input of power (or at least with only a small input of power).
What Can Increase Ceiling Fan Power Consumption?
Ultimately, a ceiling fan will consume more power if the motor works harder and this is true regardless of whether the fan has an AC motor or a DC motor. There are a number of factors influencing how hard the ceiling fan works.
Ceiling fans and their support features are designed to hold the weight of the ceiling fan and the motor is sized to power a fan of this weight. Any additional weight, particularly to the blades, will put strain on the motor because it has to work harder to produce blade rotation. To meet the increased workload, the fan must pull more power.
Even if you aren’t hanging items on your ceiling fan, something like upgrading your blades and not matching the length and weight of the previous blades can make the motor work harder and draw more power.
Drag or resistance can make a fan work harder because the motor has to expend energy overcoming the resistance or drag before the energy can be used to produce rotation. It also takes more energy to maintain a constant speed under these conditions. You create resistance if you do things like change the size of the blades or increase their pitch.
Regularly running a ceiling fan all day and night will put the motor under undue stress. Ceiling fans are designed to run for long periods of time, but closer to overnight than to a full 24 hours each day during the summer.

The more you use a ceiling fan, the more wear and tear it experiences. As motors and moving parts wear out, they function less effectively and draw more power to maintain function. Even if you used your ceiling fan as per the instructions, if it is getting to the end of its life, it will also consume more energy.
It is important to note that a ceiling fan motor can withstand some heat, but they are capable of overheating from too much stress.
AC vs DC Ceiling Fans: Efficiency Compared
Power consumption is not the only factor you should be looking at. The efficiency of a ceiling fan is also critical to its running costs and impact on the planet.
Because the rotation of ceiling fan blades is what determines the amount of airflow created, if the lower power consumption of DC ceiling fans does not translate into less airflow, then DC ceiling fans are more efficient.
It turns out that this is the case. In addition to consuming less power, DC ceiling fans are more efficient than AC ceiling fans, using the smaller wattage to produce equal or greater airflow. Ceiling fan efficiency is measured in CFM/W.
The average AC ceiling fan has an efficiency of around 75 CFM/W. The average DC ceiling fan has an efficiency of around 200 CFM/W. This is more than two times the average of an AC ceiling fan.
Sources
https://opereviews.com/battery-volts-amps-watts-ohms-law/
https://www.lightsonline.com/ceiling-fan-motor-types
https://www.universalfans.com.au/blog/dc-ceiling-fans-vs-ac-ceiling-fan-best/

