Insulating a home is one of the most important steps to undertake when creating an energy-efficient home. However, when insulating your home, it is important to know what materials are out there and which ones will be the best for your home.
Foam board insulation has a unique advantage over other types of insulation due to its closed-cell nature. However, the chemical additions to foam board can make it a dangerous addition to the home.

Foam board insulation is closed-cell, rigid, white, pink, or blue, polyurethane, polystyrene, or polyisocyanurate boards that last 100+ years. Inherent R-values are 3.6-8 per inch. The cost is $0.31-0.6 per sq. ft. Insecticides and fire-retardant chemicals are hazardous to health.
What Is Foam Board Insulation?
Foam board, also known as rigid board, is a relatively new form of insulation made of foam products that can include polyurethane, polystyrene, and polyisocyanurate.
These foam boards may also come equipped with laminated sides that can increase the endurance of the product as well as the thermal resistance.
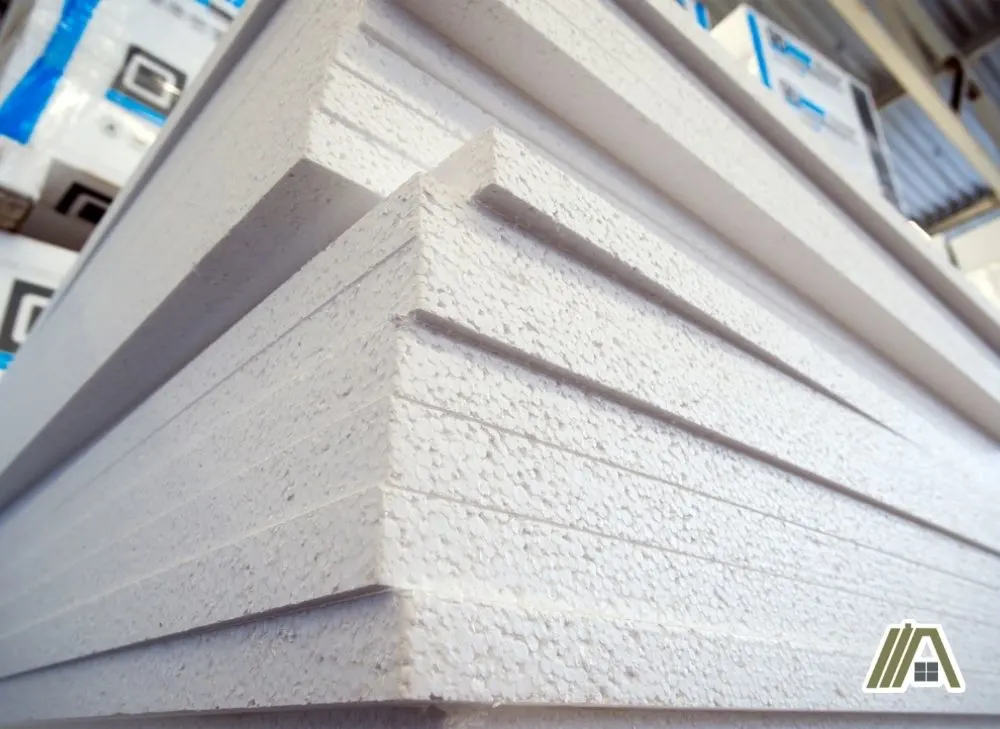

The chemical structure of this majority-foam product makes the insulation “closed-cell”, while most other types of insulation are open-cell materials.
Closed-cell basically means that the cells of the product are uniform and rigid. This is where foam board gets its alternative name and what makes them so sturdy.
By contrast, open-cell products have nonuniform cells that are less rigid, making the insulation material softer and more pliable.
The closed-cell nature of foam board insulation makes it more robust as well as water-resistant. These two factors allow foam board insulation to last 100 years or more.
The water resistance of foam board insulation makes it a great option for basements that suffer from humidity issues.
Appearance and Use
Foam board insulation is sold in large, solid sheets. They are often either 2’ by 8’ or 4’ by 8’.
This distinguishes them from other types of insulation, such as fiberglass and other open-cell types of insulation.
Open-cell insulation is often sold in rolls to save space. Foam board insulation, though, is far too rigid to fold or roll. This is especially true if the foam board is laminated.
What foam board looks like mostly depends on the type.
Polystyrene foam boards come in expanded and extruded forms. The expanded form is white. The extruded form comes in pink and blue colors and has a more lightweight design.
The polyiso and polyurethane forms are often an off-white color, with foil lining their largest faces.
Foam board insulation can be used anywhere you would use any other type of insulation. These locations include roofs, foundation walls, wall panels, and more.
Inherent R-Value of Foam Board Insulation
Depending on the type of foam board insulation, the inherent insulation R-value will vary.
The R-value of insulation basically describes how well the insulation resists the conductive flow of heat. Materials have an inherent R-value but the rating can be increased by increasing the thickness of the material.
The higher the R-value of a substance, the more insulation is possible with less thickness.
Expanded polystyrene foam boards often have an R-value of between 3.6 to 4.0 per inch of thickness.
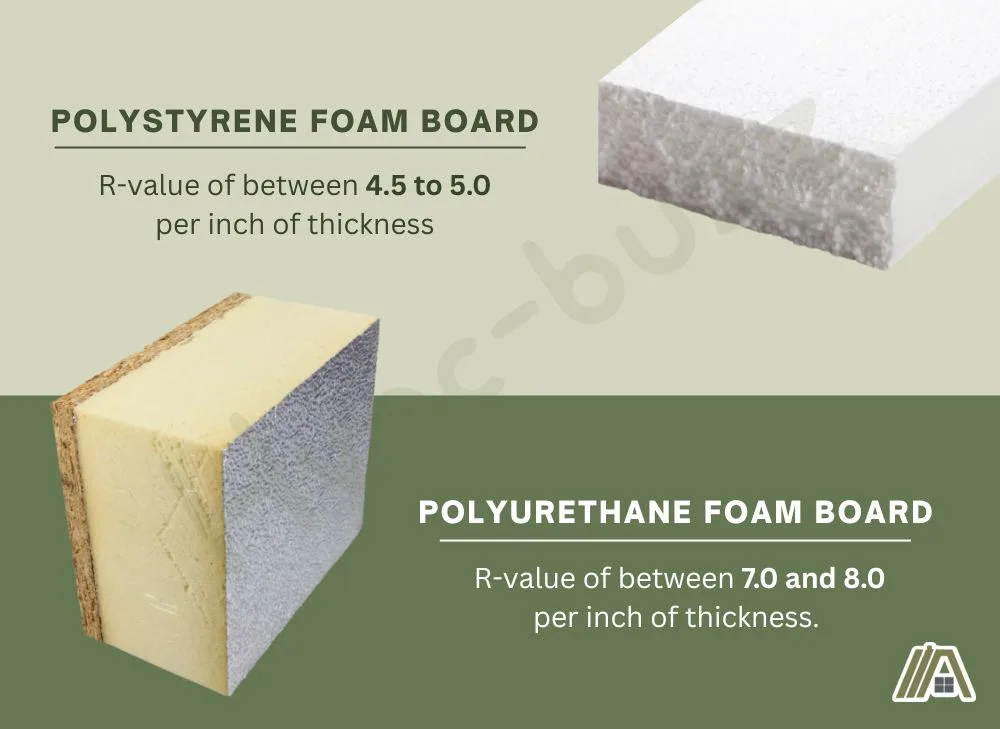
Extruded polystyrene foam boards often have an R-value of between 4.5 to 5.0 per inch of thickness.
Polyurethane and polyiso foam boards have the highest R-values of foam boards, with values between 7.0 and 8.0 per inch of thickness.
This high R-value is attributed to the low conductivity of the gases contained within the foam board’s closed cells. However, over time, these gases escape and the R-value decreases as this occurs.
Thickness Guide
The standard R-values include R30, R38, R49, and R60 with increasing insulation capacity for rising values.
However, R-values for insulation are often given in terms of RX per inch.
To find the desired thickness for standard R-values, the R-value must be divided R-value per inch.
Since R-value per inch varies by the type of foam board insulation, the thickness to achieve standard R-values will vary.
For the sake of simplicity, I will refer to extruded polystyrene since it is most commonly used. I will also use an R-value of 5.0 per inch of thickness for simplicity.
Cost of Foam Board Insulation
Just as the R-value and appearance vary by the type of foam board insulation, so too does cost.
A foam board of a one-inch thickness is used below for cost estimates.
- Expanded polystyrene costs about $0.31 for a square foot of the material. This is the cheapest form of foam board insulation.
- Extruded polystyrene costs about $0.47 for a square foot of the material.
- Polyiso foam board costs about $0.60 for a square foot.
- Polyurethane foam board costs about the same as polyiso foam board.
Is It Easy to Install?
As was mentioned before, foam board insulation is much more rigid than other types of insulation that use open-cell materials. This can create problems but can also provide ease in installation.
When carrying the material into the home, a large 4’ by 8’ board can be difficult to get through doorways, which can lead to damage to the material.
The lack of flexibility can also make it difficult to install since the material would not be able to be maneuvered around tight spaces while installing it. To make things fit, the material may need to be cut, while a non-rigid board could be bent or folded.
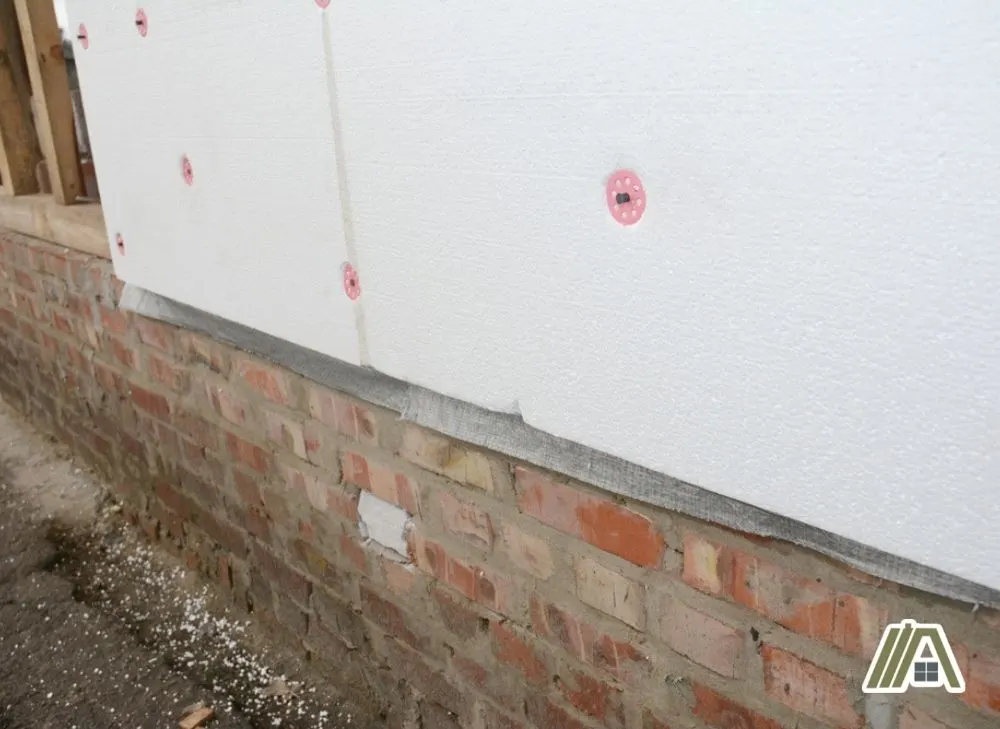

However, foam board’s ability to keep its shape comes in handy when installing since, once it is installed, it will not move or fold in on itself as other insulation might.
Given these tradeoffs, foam board insulation can be installed somewhat easily if you have enough space.
One tip to keep in mind is that, when choosing the thickness of your foam board, you should find a happy medium between your desired R-value and a thickness that will lead to ease of installation, since too thick of foam board can make it difficult to hit studs when driving in screws.
Is Foam Board Insulation Dangerous?
Although the addition of flame retardant to foam board insulation can prove very useful in preventing the spread of a fire, the chemicals used to do this can be dangerous to human health.
These toxic flame retardants include HBCD and TCPP, which are both highly toxic and hard to get rid of.
- HBCD is included in both extruded and expanded polystyrene foam boards.
- TCPP is included in polyiso foam boards.
Although most manufacturers are trying to steer clear of these additives, they may still be contained in foam boards.
Another addition to foam board that can be useful but dangerous is the inclusion of insecticide, specifically for termites.
Insecticides can be hazardous to human health and can also hurt important pollinators like bees.
Foam board production may also be a threat to global health since the manufacturing process uses a blowing agent called XPS, which is 1,430 times more potent of a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide.
Benefits of Foam Board Insulation
- Compared to other kinds of insulation, certain kinds of foam boards have a fairly high R-value.
- Foam boards are more robust than other kinds of insulation, making them stronger.
- Rigid board insulation is quite good at keeping moisture out of the home, which is great for basements.
- Foam boards can last more than 100 years.
- The rigidity of foam boards means that they keep their shape while being installed, making them stay in place easier.
- Some foam boards contain flame retardant and insecticide, which can limit the damage by fire and termites to your home.

Drawbacks of Foam Board Insulation
- They are often more expensive than other types of insulation.
- The R-value of the foam board insulation can deteriorate over time in polyiso and polyurethane boards as the gases escape.
- The rigidity of the boards can make their transport, storage, and installation difficult as they are not able to fold or bend.
- Foam boards’ flame-retardant additions mean that toxic chemicals may leak into the home.
- When a foam board contains insecticide, the chemicals can cause harm to humans as well as important pollinators such as bees.
- The manufacturing process that produces foam boards releases a chemical that accelerates global warming.
Sources
https://www.progressivefoam.com/open-cell-vs-closed-cell-insulation/
https://garynsmith.net/how-to-install-rigid-foam-to-the-outside-a-house/
https://www.finehomebuilding.com/2012/01/24/buyers-guide-to-insulation-rigid-foam
